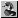    | DocBook: The Definitive Guide 2.0.17 (Alpha) |
$Revision: 5565 $
$Date: 2006-02-16 08:50:26 -0500 (Thu, 16 Feb 2006) $
imagedata — Pointer to external image data
imagedata ::= EMPTY
Name | Type | Default | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| width | CDATA | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| srccredit | CDATA | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| contentdepth | CDATA | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| entityref | ENTITY | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| contentwidth | CDATA | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| scalefit | CDATA | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| align |
| None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| valign |
| None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| depth | CDATA | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| fileref | CDATA | None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| format |
| None | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| scale | CDATA | None |
This element points to an external entity containing graphical image data.
Render the image. May be formatted inline or as a displayed block, depending on context.
There are two ways to provide content for ImageData:
EntityRef or FileRef. It is best to use only one of these
methods, however, if multiple sources are provided,
EntityRef will be used in favor of
FileRef.
ImageData provides a selection of attributes
that can be used to control how the image is rendered. These
attributes define two rectangles, the viewport
area and the content area, and how
these rectangles are related to each other. The intrinsic
size of the image is a third rectangle that sometimes
influences the way an image is rendered.
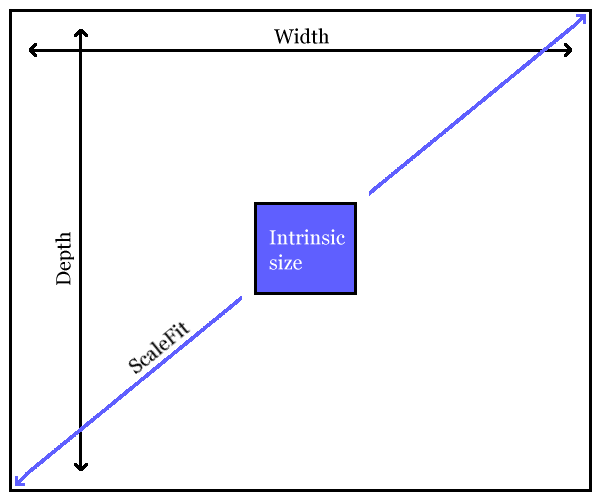
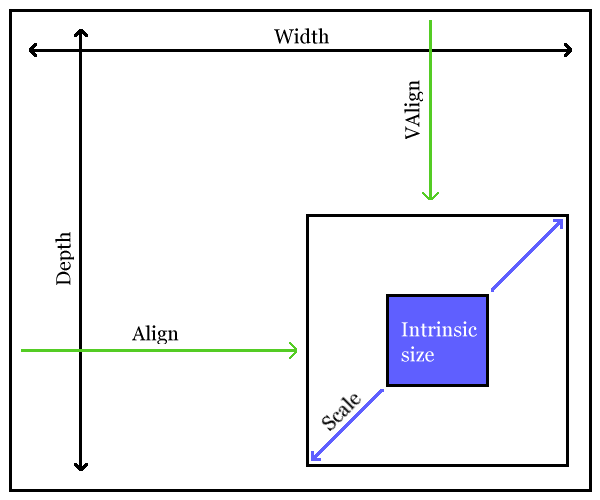
It is important to understand the distinction between these three areas. When rendering an image, the viewport area defines the space reserved in the flow of content for the image. If a 6in x 4in viewport area is specified, that's how much space will be reserved for the image, independent of the actual size of the rendered image. The content area defines the actual size of the rendered image, independent of the intrinsic size of the image. The intrinisic size of the image is its actual, real size.
DocBook provides three mutually exclusive mechanisms for specifying the content area of an image: it can be specified directly, it can be specified by selecting a scale factor, or it can be specified to be the same size as the viewport area.
Finally, DocBook provides two attributes,
align and
valign to specify the alignment of
the content area within the viewport area.
DocBook provides no mechanism for specifying how an image should be rendered if the content area exceeds the viewport area in either or both dimensions. Implementations are free to perform clipping, allow the image to overflow, and/or generate errors.
The size of the viewport area and the content area are defined in terms of lengths (width and depth).
Lengths must be expressed as a decimal value followed immediately by an optional unit of measure or a percentage. Six and one eight inches, for example, must be expressed as “6.125in”. It is an error to put a space or other punctuation between the decimal value and the unit of measure.
Examples of common units of measure include:
pt | Points (1/72 of an inch) |
cm | Centimeters |
mm | Millimeters |
in | Inches |
pc | Picas (1/6 of an inch) |
px | Pixels |
em | Ems |
If no unit of measure is provided, px is
assumed. Note that pixels have no universally accepted absolute size
and ems are relative units of measure. Implementations may define
pixel sizes differently and stylesheets may or may not be able to
determine the current font size in order to correctly calculate the
absolute size of an em. It is best to avoid these units of
measure.
Percetages are expressed as a decimal value followed immediately by
a % sign.
The viewport area is specified by the width and depth attributes.
If neither width nor depth is specified, an implementation is free to choose defaults. These defaults may be influenced by context. For example, when rendering an inline graphic, the viewport area often defaults to the size of the content area. For block graphics, the width often defaults to the column width while the depth defaults to the depth of the content area.
If only one of width or depth is specified, an implementation is free to choose a default for the other dimension.
Viewport area dimensions expressed as a percentage are a percentage
of the available area. For example, a width of 50%
when an implementation is rendering in a column 6in wide is equivalent
to specifying a width of 3in.
Percentages must be used with care. Some media are unbounded in one or more directions (for example, web pages are generally unbounded in depth). Specifying a percentage of an unbounded dimension is undefined. Implementations may choose arbitrary defaults or may generate errors.
The content area is specified by the contentwidth and contentdepth attributes.
If neither content width nor content depth is specified, an
implementation is expected to render the image at its intrinsic size
(unless scaling or scaling to fit is requested).
If only one of content width or content depth is specified, an
implementation is expected to choose a default for the other dimension
such that the image is scaled proportionally. For example, if an image
has an intrinsic size of one square inch and the content width is
specified as 2in, the content depth must default to
2in.
Content area dimensions expressed as a percentage are a percentage of the intrinsic size of the image.
Percentages must be used with care. Some implementations may be unable to determine the intrinsic size of an image and will therefore be forced to make compromises. Implementations may choose arbitrary values or may generate errors if the intrinsic size cannot be obtained.
There are two ways that scaling can be specified, with the
scale attribute or with the
scalefit attribute.
If scale is specified, it must be a positive integer. It
is always interpreted to be a percentage value where
“100” represents 100%.
The legal values of scalefit are 0 (false)
or 1 (true). If scaling to fit is requested, the
content area is scaled until either the content
width is the same as the viewport width (and the content depth is less
than or equal to the viewport depth) or the
content depth is the same as the viewport depth (and the content width
is less than or equal to the viewport width), whichever comes first.
In other words, scaling to fit never causes anamorphic scaling, it
simply scales the image as large as possible without overflowing the
bounds of the viewport area.
Specification of content area, scaling, and scaling to fit are
mutually exclusive. If a content area (contentwidth, contentdepth, or both) is specified,
both scaling and scaling to fit are ignored. If
the content area is not specified and both scaling and scaling to fit
are specified, scalefit is
ignored.
In order to achieve a level of backwards compatibility with previous
versions of DocBook (which did not have attributes for specifying a content
area) while maintaining coherent semantics, the default value of
scalefit depends on other attributes:
| Viewport area | Content area | scalefit default |
|---|---|---|
| unspecified | unspecified | irrelevant |
| specified | unspecified | 1 |
| unspecified | specified | 0 |
| specified | specified | 0 |
If a viewport area is specified (and neither a content area nor scaling
is specified) and scalefit is explicitly
“0”, the viewport area specification must
be ignored.
Two alignment attributes are provided,
align and
valign.
If specified, align indicates how
the content area should be aligned horizontally within the viewport area. If
not specified, implementations are free to choose any default value.
If specified, valign indicates how
the content area should be aligned vertically within the viewport area. If
not specified, implementations are free to choose any default value.
If nothing is specified about the size of an image, it is rendered in a content area that is the same as its intrinsic size in a viewport area that is implementation defined:
<imagedata fileref="image.png"/>

If a viewport area is specified, the image is rendered in a content area that is the same as its intrinsic size in the specified viewport area:
<imagedata fileref="image.png" width="6in" depth="5.5in" scalefit="0"/>
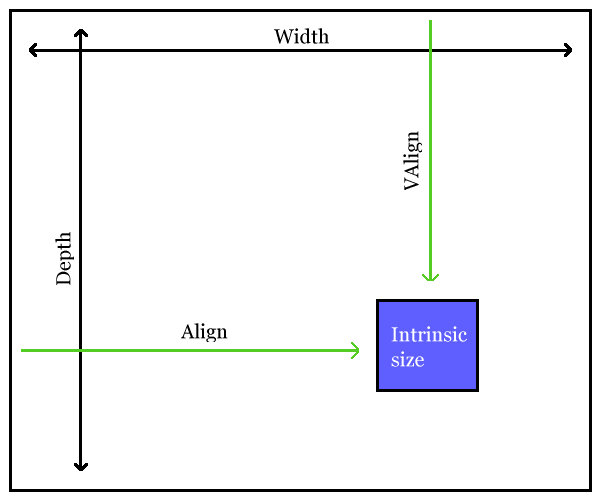
If a content area is specified, the image is scaled (possibly anamorphically) to that size and rendered in a viewport area that is implementation defined:
<imagedata fileref="image.png" contentwidth="4in" contentdepth="3in"/>
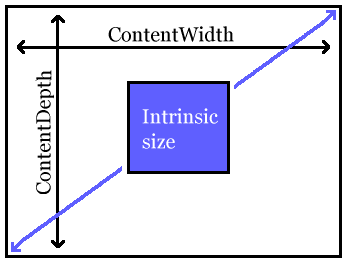
If a scaling factor is specified, the intrinsic size is scaled uniformly by that amount to obtain the content area which is rendered in a viewport area that is implementation defined:
<imagedata fileref="image.png" scale="300"/>
If a viewport area is specified and scaling to fit is requested, the intrinsic size is scaled (uniformly) as large as possible without extending beyond the bounds of the viewport area which is rendered as specified.
<imagedata fileref="image.png" width="6in" depth="5.5in"/> <!-- note that scalefit="1" is the default in this case -->
If the viewport area and content area are specified, the image is scaled (possibly anamorphically) to the content area size and rendered in the specified viewport area:
<imagedata fileref="image.png" width="6in" depth="5.5in"
contentwidth="4in" contentdepth="3in"/>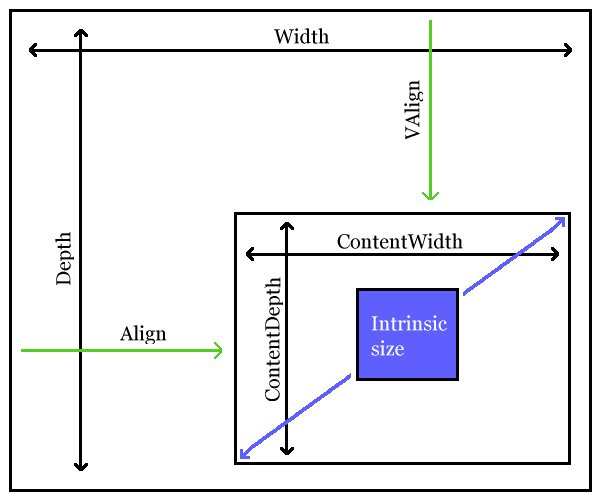
If the viewport area and a scaling factor are specified, the intrinsic size is scaled uniformly by the scaling factor amount to obtain the content area which is rendered in the specified viewport area:
<imagedata fileref="image.png" width="6in" depth="5.5in" scale="300"/>
Align specifies the horizontal alignment
of the content area in the viewport area.
ContentDepth specifies the desired depth of the
content area.
ContentWidth specifies the desired width of the
content area.
Depth specifies the desired depth of the
viewport area.
EntityRef identifies the general entity
which points to the content of the image data.
FileRef specifies the name of the file
which contains the content of the image data.
Format identifies the format of the image
data. The Format must be a defined
notation.
Scale is an integer representing
a percentage scaling factor (retaining the relative dimensions of the
original image). If unspecified, the value 100 (100%) is
assumed.
If ScaleFit has the value 1 (true), then
the image data is to be scaled (uniformly) to the specified width or depth.
The default value of 0 (false) indicates that the image will not be
scaled to fit (although it may still be scaled by the
Scale attribute).
SrcCredit contains details about the source
of the image data.
Width indicates the width of the graphic.
For examples, see
imageobject, informalfigure, inlinemediaobject, mediaobjectco, videoobject.