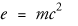inlinemediaobject
inlinemediaobject — An inline media object (video, audio, image, and so on).
Synopsis
inlinemediaobject ::=
Attributes
Description
The inlinemediaobject element contains a set of
alternative “graphical objects”: videoobject,
audioobject, and imageobject.
Additional textual descriptions may be provided with
textobjects.
An inlinemediaobject provides a wrapper for a
set of alternative presentations for some, usually graphical,
information. It is the “inline” equivalent of
mediaobject.
In almost all contexts where text is allowed,
inlinemediaobject is also allowed. This allows an
author to provide a graphic for a character or glyph—for example, one
that is not available in the publisher’s fonts or perhaps is not
available in Unicode. Authors should exercise care when using
inlinemediaobject for this purpose as graphics may be
difficult or impossible to display in some contexts on some presentation
systems.
Processing expectations
Formatted inline.
If possible, the processing system should use the content of the
first object within the inlinemediaobject. If the
first object cannot be used, the remaining objects should be
considered in the order that they occur. A processor should use the
first object that it can, although it is free to choose any of the
remaining objects if the primary one cannot be used.
Under no circumstances may more than one object in an
inlinemediaobject be used or presented at the same
time.
For example, an inlinemediaobject might
contain a high-resolution image, a low-resolution image, and a text
description. For print publishing, the high-resolution image is used;
for online systems, either the high- or low-resolution image is used,
possibly including the text description as an online alternative. In a
text-only environment, the text description is used.
Parents
60 elements contain inlinemediaobject. × ⏵
Children
6 elements occur in inlinemediaobject. × ⏵
See Also
Related elements: audioobject, caption, imageobject, mediaobject, textobject, videoobject.
Examples
1 |<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>|<article xmlns="http://docbook.org/ns/docbook">|<title>Example inlinemediaobject</title>|5 |<para>Einstein's most famous equation,|<inlineequation>|<inlinemediaobject>|<imageobject condition="print">|<imagedata fileref="figs/print/db5d_refeqn03.pdf"/>10 |</imageobject>|<imageobject condition="web">|<imagedata fileref="figs/web/db5d_refeqn03.png"/>|</imageobject>|<textobject>15 |<phrase>E=mc<superscript>2</superscript></phrase>|</textobject>|</inlinemediaobject>|</inlineequation>, expresses the relationship between matter and energy.|</para>20 ||</article>
Einstein's most famous equation,