equation
equation — A displayed mathematical equation.
Synopsis
equation ::=
- Sequence of:
Attributes
Common attributes and common linking attributes.
Additional attributes:
- floatstyle
- label
- pgwide (enumeration)
- “0”
- “1”
- type
Additional Constraints
- example must not occur among the children or descendants of equation
- figure must not occur among the children or descendants of equation
- table must not occur among the children or descendants of equation
- equation must not occur among the children or descendants of equation
- If this element is the root element, it must have a version attribute.
Description
An equation is a formal mathematical equation
(with an optional rather than a required title).
If the MathML Module is used, equation can also
contain the mml:math
element.
Processing expectations
Formatted as a displayed block. For an inline equation, use
inlineequation.
Processing systems that number equations or build a table of
equations at the beginning of a document may have difficulty correctly
formatting documents that contain both equations
with titles and equations
without titles. You are advised to use informalequation for equations without
titles.
Attributes
Common attributes and common linking attributes.
- any attribute
-
Any attribute in any other explicit namespace
- floatstyle
-
Specifies style information to be used when rendering the float
- label
-
Specifies an identifying string for presentation purposes
- pgwide
-
Indicates if the element is rendered across the column or the page
Enumerated values: “0” The element should be rendered in the current text flow (with the flow column width).
“1” The element should be rendered across the full text page.
- type
-
Identifies the type of equation
Parents
These elements contain equation: abstract, acknowledgements, annotation, answer, appendix, article, bibliodiv, bibliography, bibliolist, blockquote, callout, calloutlist, caption (db.caption), caution, chapter, colophon, constraintdef, danger, dedication, entry, example, figure, footnote, formalgroup, glossary, glossdef, glossdiv, glosslist, important, index, indexdiv, informalexample, informalfigure, itemizedlist, legalnotice, listitem, meta (db.meta.content), msgexplan, msgtext, note, orderedlist, para, partintro, preface, procedure, qandadiv, qandaset, question, refsect1, refsect2, refsect3, refsection, refsynopsisdiv, result, revdescription, sect1, sect2, sect3, sect4, sect5, section, setindex, sidebar, simplesect, step, taskprerequisites, taskrelated, tasksummary, td, textobject, th, tip, toc, tocdiv, topic, variablelist, warning.
Children
The following elements occur in equation: alt, caption (db.caption), info (db.titleforbidden.info), info (db.titleonly.info), mathphrase, mediaobject, mml:*, title, titleabbrev.
See Also
Related elements: example, figure, informalequation, informalexample, informalfigure, informaltable, inlineequation, subscript, superscript, table.
Examples
1 |<article xmlns='http://docbook.org/ns/docbook'>|<title>Example equation</title>||<equation xml:id="eq.fermat">5 |<title>Fermat's Last Theorem</title>|<alt>x^n + y^n ≠ z^n ∀ n ≠ 2</alt>|<mediaobject>|<imageobject condition="print">|<imagedata fileref="figs/print/db5d_refeqn01.pdf"/>10 |</imageobject>|<imageobject condition="web">|<imagedata fileref="figs/web/db5d_refeqn01.png"/>|</imageobject>|</mediaobject>15 |</equation>||</article>
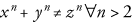
Alternatively, for relatively simple equations such as Fermat's Last
Theorem, mathphrase is often sufficient:
1 |<article xmlns='http://docbook.org/ns/docbook'>|<title>Example equation</title>||<equation xml:id="eq.fermat.mathphrase">5 |<title>Fermat's Last Theorem</title>|<alt>x^n + y^n ≠ z^n ∀ n ≠ 2</alt>|<mathphrase>x<superscript>n</superscript>|+ y<superscript>n</superscript>|≠ z<superscript>n</superscript>10 |∀ n ≠ 2</mathphrase>|</equation>||</article>